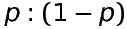Theorem 1
If A and B are events associated with a random experiment having sample space S and if 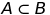 , then
, then
lessthanequalP(B).png)
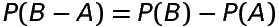
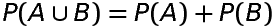 If
If 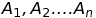 are mutually exclusive events associated with a random experiment, then
are mutually exclusive events associated with a random experiment, then
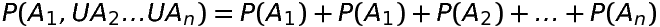
Theorem 2
If A and B are mutually exclusive and exhausive events associated with a random experiment having sample space S, then
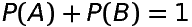
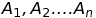 are mutually exclusive and exhaustive events associated with
random experiment having sample space S, then
are mutually exclusive and exhaustive events associated with
random experiment having sample space S, then
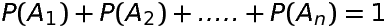
Theorem 3
If A and B are any two events associated with a random experiment having sample space S, then
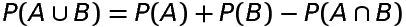
Theorem 4
If A and B are any two events associated with a random experiment, then
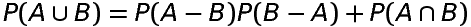
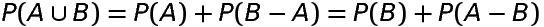
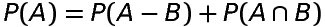
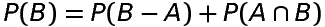
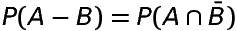 Probability of occurence of A only
Probability of occurence of A only
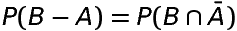 Probability of occurence of B only
Probability of occurence of B only
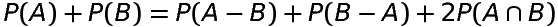
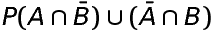 is the probability of occurence
of only (or exactly) one of the two events A and B.
is the probability of occurence
of only (or exactly) one of the two events A and B.
Theorem 5
If A, B and C are any three events associated with a random experiment, then
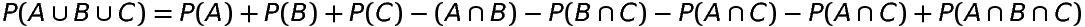
Other Important Properties


If odds in favour of an event A are a:b then
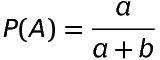 If odds against an event A are a:b then
If odds against an event A are a:b then
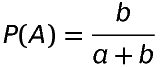 If probability of an event is p then odds in favour are
If probability of an event is p then odds in favour are